Hard x-ray imaging by Multilayer Zone Plates
Combined Optics and Sample Tower
X-ray focusing onto sample
The incoming x-ray beam with a slit-defined size on the order of 100 µm is pre-focused to match roughly the MZP aperture of around 10 µm diameter; for pre-focusing, we usually utilise Kirkpatrick-Baez mirrors or compound refractive lenses.
An MZP is a focusing optic of the diffractive kind; to first order it can be described as an axialsymmetric grating with a gradient. This gradient changes the (Laue) diffraction angle along its aperture to direct to the common focal spot.
Apart from this +1st order focus, also other odd focal spots with reduced focal lengths, and purely diverging negative orders, exist.
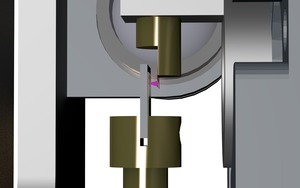
Close-up of the x-ray beam (shown in magenta), focused by the MZP (mounted e.g. on a TEM grid attached to a diffractometer pin hanging from above) onto the sample, mounted e.b. on a silicon nitride membrane (Rendering).